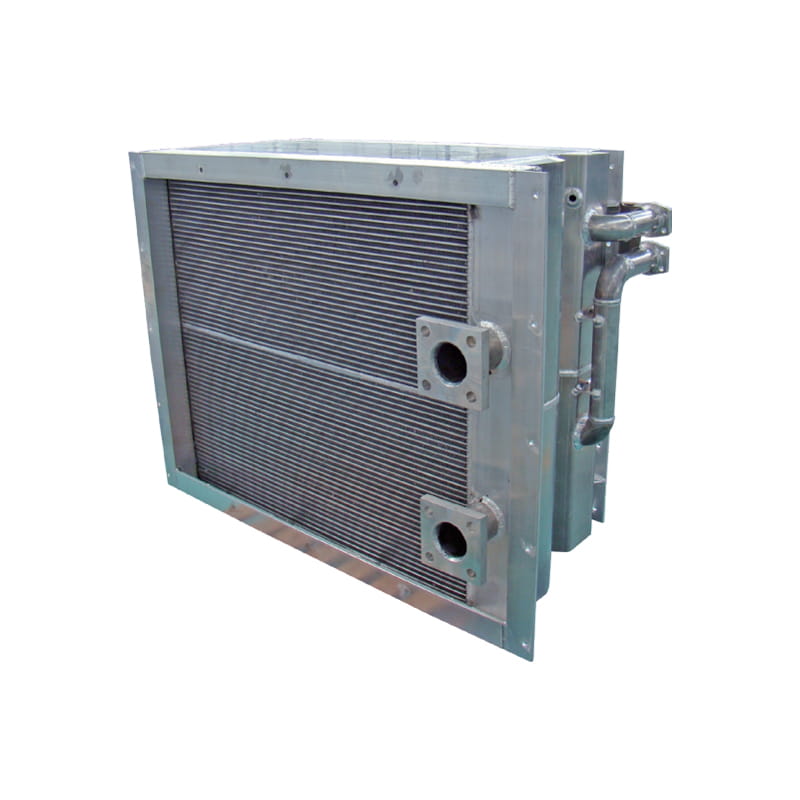
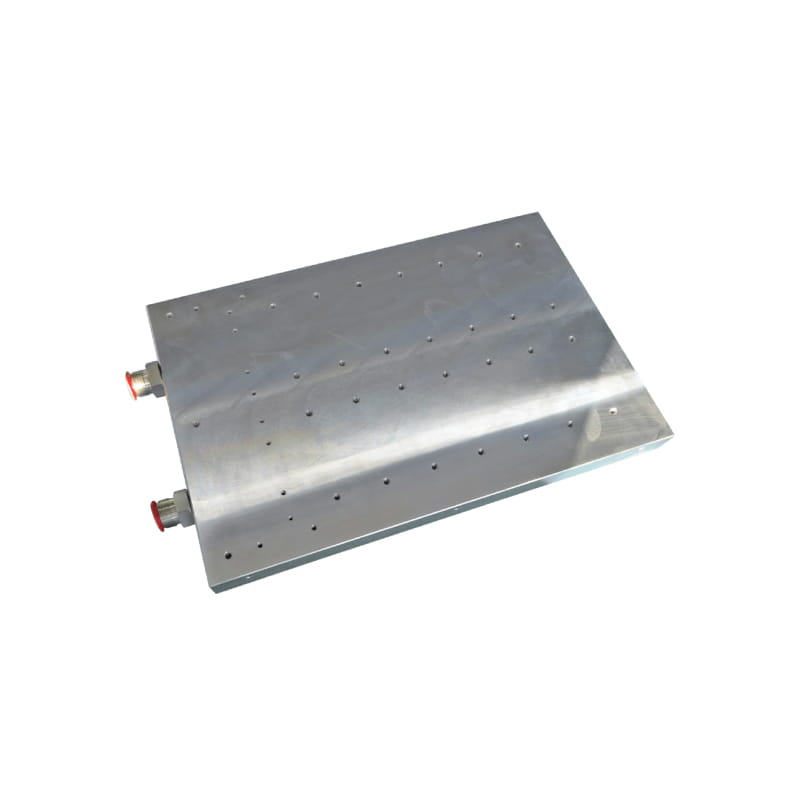
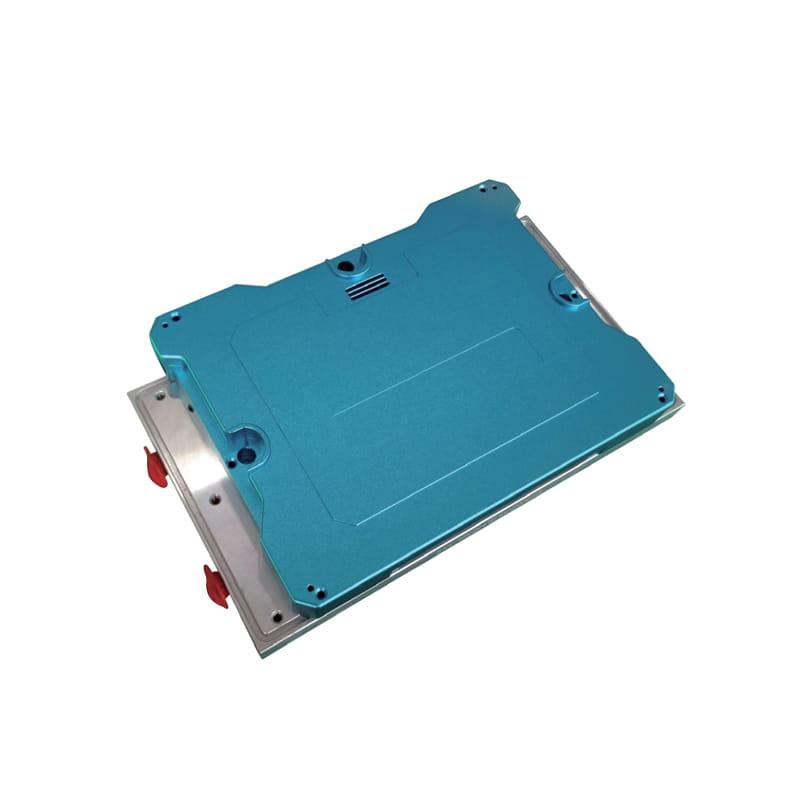
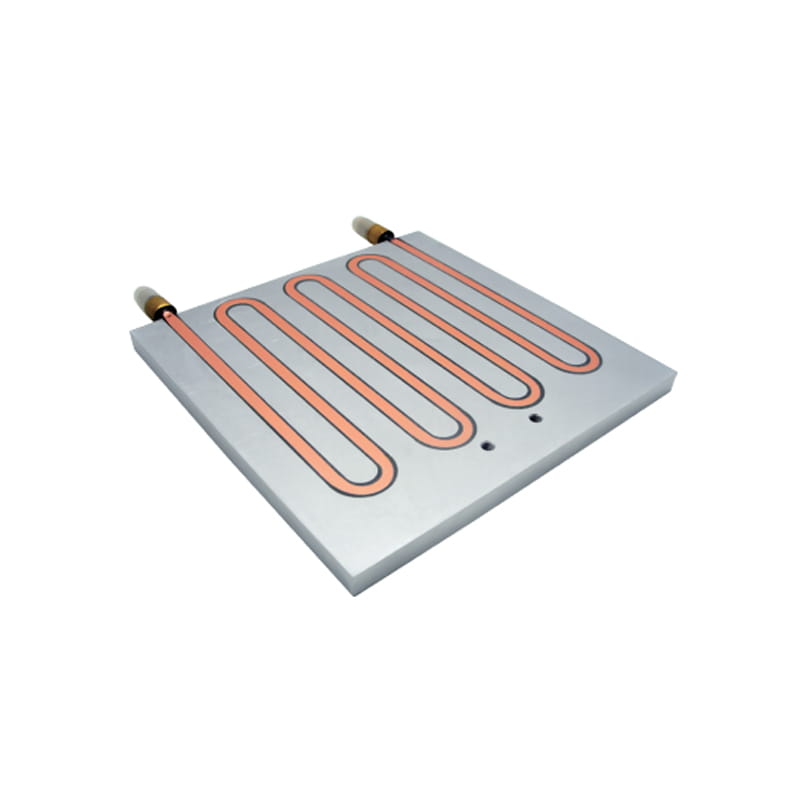
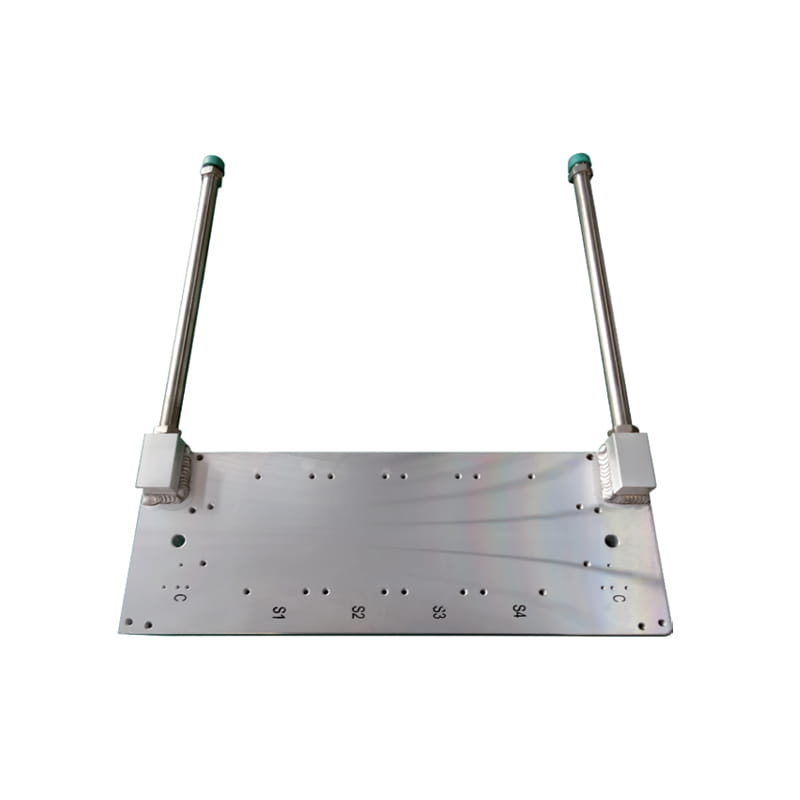
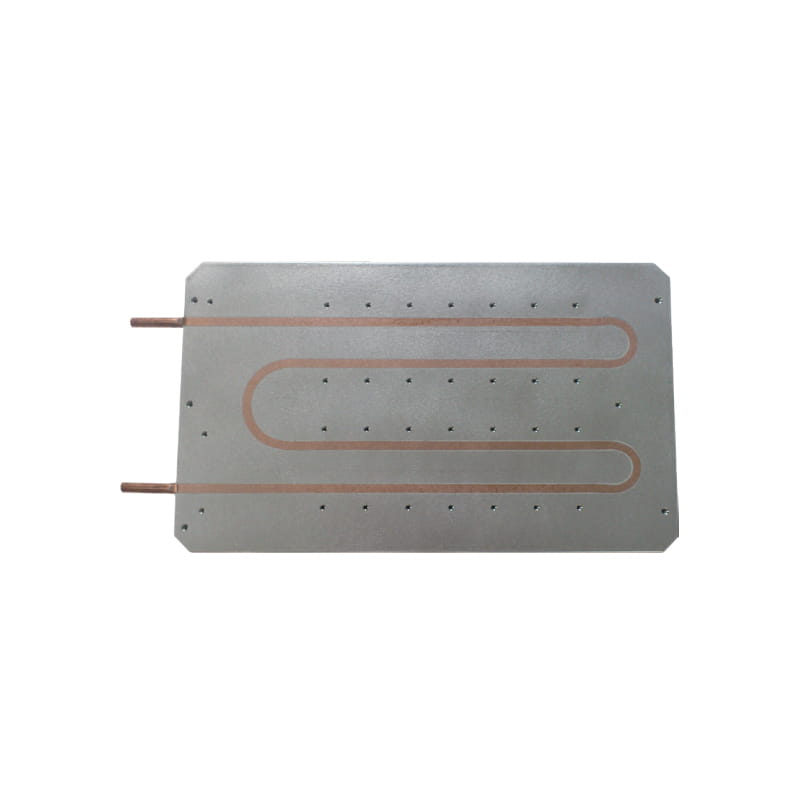
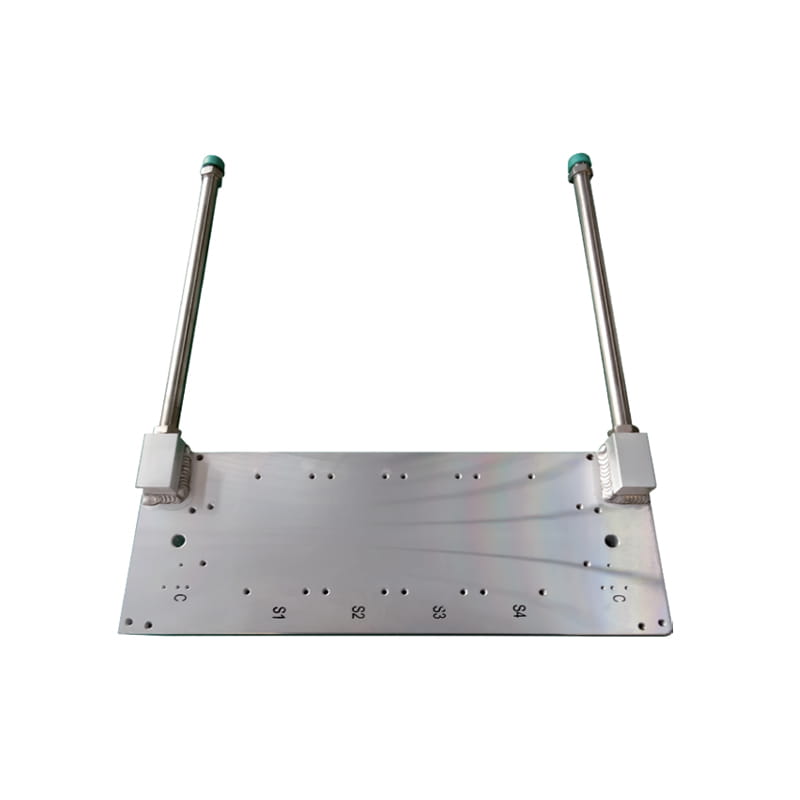
Heat Load: Determine the amount of heat that needs to be dissipated from the heat source (e.g., electronic components). This is typically measured in watts (W) or BTUs per hour (BTU/hr).
Flow Rate: Calculate the required flow rate of the cooling fluid (e.g., water or coolant) through the cold plate to efficiently carry away the heat. This is usually measured in liters per minute (LPM) or gallons per minute (GPM).
Pressure Drop: Evaluate the pressure drop across the liquid cold plate, which refers to the decrease in fluid pressure as it flows through the plate. High pressure drop can result in decreased flow rates and increased pumping power requirements.
Size Constraints: Consider the physical dimensions and space limitations of the application environment. Choose a liquid cold plate that fits within the available space while still providing adequate cooling capacity.
Compatibility with Cooling Fluids: Ensure that the materials used in the construction of the cold plate are compatible with the cooling fluid being used. For example, certain materials may corrode or degrade when exposed to specific types of fluids or additives.
Thermal Resistance: Assess the thermal resistance of the liquid cold plate, which is a measure of how effectively it transfers heat from the heat source to the cooling fluid. Lower thermal resistance indicates better heat transfer performance.

Material Selection: Choose the appropriate material for the cold plate based on factors such as thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and cost. Copper and aluminum are commonly used materials due to their excellent thermal properties.
Channel Design: Consider the design of the internal flow channels within the cold plate, including the number, shape, and arrangement of channels. Optimize the channel design to maximize heat transfer and minimize pressure drop.
Environmental Conditions: Take into account the operating environment conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants. Select a liquid cold plate that can withstand the environmental conditions without compromising performance or reliability.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose the right liquid cold plate that meets the specific cooling requirements of your application while considering performance, efficiency, and durability.

 English
English русский
русский